The worldwide push toward sustainability has thrust carbon credits into the heart of corporate and governmental Climate change fighting plans. Yet today’s carbon credit markets are plagued by issuers trading in opacity, double counting, and suboptimal validation.
Here is where blockchain can help. We are utilizing blockchain to symmetrize carbon credits; tokenizing, storing and trading of them on a registries – making such credits theoretically traceable, and significantly slashing shady practices on the carbon market, effectively enabling businesses of any size to buy, sell, or retire these without encountering bureaucratic or financial barriers.
This guide will take you through the steps to create a blockchain carbon credit platform, as well as demonstrate projects that are already doing it, and answer the big questions we hear most.
But before we get into how to build a carbon credits platform, we should discuss what makes blockchain such a great tool for managing carbon tokens:
Begin by determining whom you are creating the platform for and what problem it solves.
Here are a few possible goals:-
Also, consider what type of network you want to use: Will it be a public blockchain such as Ethereum, Polygon, or BNB Chain, or will you opt for a private or consortium chain with limited access?
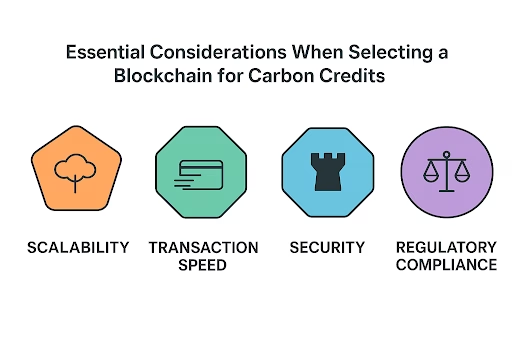
Scalability, cost, and adoption are dictated by blockchain architecture. Options include:
EVM-Compatible Chains (Ethereum, Polygon, Avalanche) : Excellent for interoperability & smart contracts. Famous for its strong smart contract functionality and large development community, Ethereum is a public blockchain. Scalability and transaction speed are the ones that bother people when using it, since it provides transparency/shared ledger and decentralization.
Private Permissioned Chains (Hyperledger Fabric, Quorum) : For Governments and enterprises who are interested in control. Hyperledger Fabric is a blockchain framework intended for enterprise applications that offers a modular architecture. It provides private transactions and confidential contracts, perfect for businesses who want to protect sensitive data. Its scalability and support for pluggable consensus mean that organizations can adapt the system to their own requirements.
Corda: Designed for financial institutions, Corda is a permissioned blockchain with a focus on privacy and transactions directly between parties. Because of its special consensus mechanism, relevant parties could access transaction records for the purpose of enhancing the privacy protection.
Carbon credits must have a digital form to be traded on blockchain. Tokenization transforms each of the verified credits (which is usually 1 ton of CO₂) into a digital asset:
ERC-20 tokens : To fungible carbon credits (This is for the purpose of general trading).
ERC-721 NFTs : Unique credits paired w/ certain projects & complete with metadata (project location, details about the project, verification docs).
Example: You have a reforestation project in Brazil which generates 10,000 credits, you now have 10,000 NFTs with geo-tagging + verification documents.
Benefits of Tokenization:
For an effective carbon credit blockchain platform, we required a few important modules:
Carbon Credit Issuance Module
Marketplace & Trading Exchange
Registry & Retirement System
Verification & Compliance Tools
User Wallet Integration
Smart contracts are contracts with terms written directly into code. In carbon credit trade, smart contracts are able to automatize the operations concerning the release, transfer, and retirement of carbon credits through predefined conditions. The automation of these processes reduces intermediary intervention, transaction costs, and time as well.
A business looking to offset its emissions, for example, might negotiate a smart contract which automatically buys the necessary credits when certain constraints are met (which simplifies the process and guarantees that the business remains in compliance).
Smart contracts are the Lego bricks of automation:
This eliminates intermediaries and reduces costs.
In order to gain trust, platforms have to provide an easy way for the stakeholders to verify the credits. Transparency features include:
Scalability is important as potentially thousands of credits could be issued per day.
Security measures:
Once the platform is ready:
These examples show the growing adoption of blockchain in climate solutions.
It is an expensive proposition to create a sophisticated carbon trading system. The final price depends on the location of your development team, the functionality of your platform, the blockchain you pick and whether or not you. It’s easy to become bogged down in the weeds of pricing, however, be it a white label carbon credit platform, or a customized one-of-a-kind project built from the ground up. Prices can vary from $60,000 for standard platforms to over $200,000 for comprehensive solutions.
The carbon credits market can be revolutionized by blockchain technology, which can make it transparent, less convoluted, efficient, and fraud-proof. From tokenized credits, to facilitating frictionless trading across the globe, blockchain-based platforms guarantee trust and scalability in combating climate change.
We at TechAroha are professionals in providing customized blockchain solutions including carbon credits platform, tokenization infrastructure and ESG solutions. We integrate sustainability with state-of-the-art blockchain technology to enable businesses, governments and NGOs to create the climate markets of the future.
What is a blockchain-based carbon credit platform?
A digital platform based on blockchain technology for financing of carbon credits and withdrawal of those from trading with traceability and full transparency.
How does tokenizing carbon credits work?
Every credit is then tokenized into a digital token (fungible ERC-20 or NFT ERC-721) and is a crypto-certificate of 1T of CO₂ removed or avoided.
Why build carbon credits on the blockchain and not traditional registries?
Facilitate global access independently through Blockchain; it is double counted proof and resistant against antisocial activities.
Is it possible for people to buy carbon credits on these platforms?
Yes. Several open ledgers let people buy small increments of credits to compensate for their carbon consumption.
Which industries benefit most from blockchain-based carbon platforms?
The beneficiaries are energy, manufacturing, transportation, fintech and ESG-driven companies.
What technologies are used to build carbon credit platforms?
Common tech stacks include Solidity, Polygon, Ethereum forks, Web3.js, React.js, IPFS, and AWS for scalable infrastructure.
Are blockchain carbon credits recognized by regulators?
Recognition does occur, but it requires alignment with the standards such as Verra, Gold Standard or government registries.