

In the last session of BlockChain Fundamentals, we have discussed “What is Block Chain”, here in the session we will discuss Block Chain in Details.
Let’s go through the definition of Block Chain
“Block Chain is a growing distributed peer to peer ledger which keeps the transaction record in chronological order which is secure and immutable”
Let’s understand the Block Chain Definition in Detail. First, we will try to understand the block and how transaction as stored in the Block Chain
It will look like below images
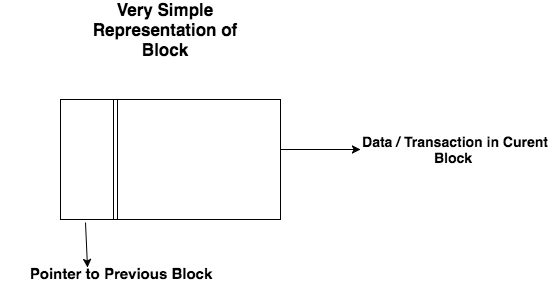
What is Block Zero(0) or Genesis Block
Whenever any blockchain project or cryptocurrency is launched it starts with the 1st Block of the Network. People often called it as genesis block or block 0.
Assume user
X -> Rs. 200
Y -> Rs. 500.
So we will store this information in Block Chain using secure military grade algorithms. After our empty genesis block, a new block will be added. Our Block Chain will network will look like below image.
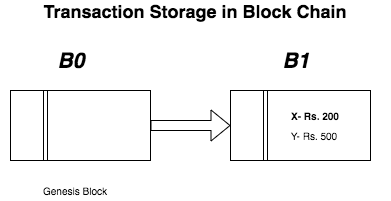
“The information that X has Rs. 200 and Y have Rs. 500 is stored permanently in blockchain block B1 and nobody can be modified it.It Permanent”
Now assume Y want’s to give Rs. 100
Now in general databases like MySQL or Oracle the, there would a field called as balance amount and it would be updated according to transaction taken. But this is not the case with Block Chain. Initial storage cannot be modified.
Instead, a block will be created which will store the detail of the transaction. This new block will also have information about the new balances of User X and User Y. Below image will describe the transaction storage.
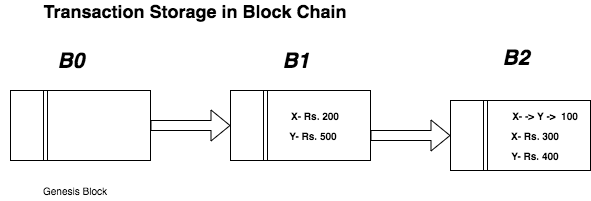
This is how new block will be added for a single or set of transactions.
“Now we see Block Chain has stored the information securely and in chronological order”
Since Block store the hash of the previous block, it creates a chain, a chain of blocks called as blockchain.
Please view the video for more clear understanding